All Categories
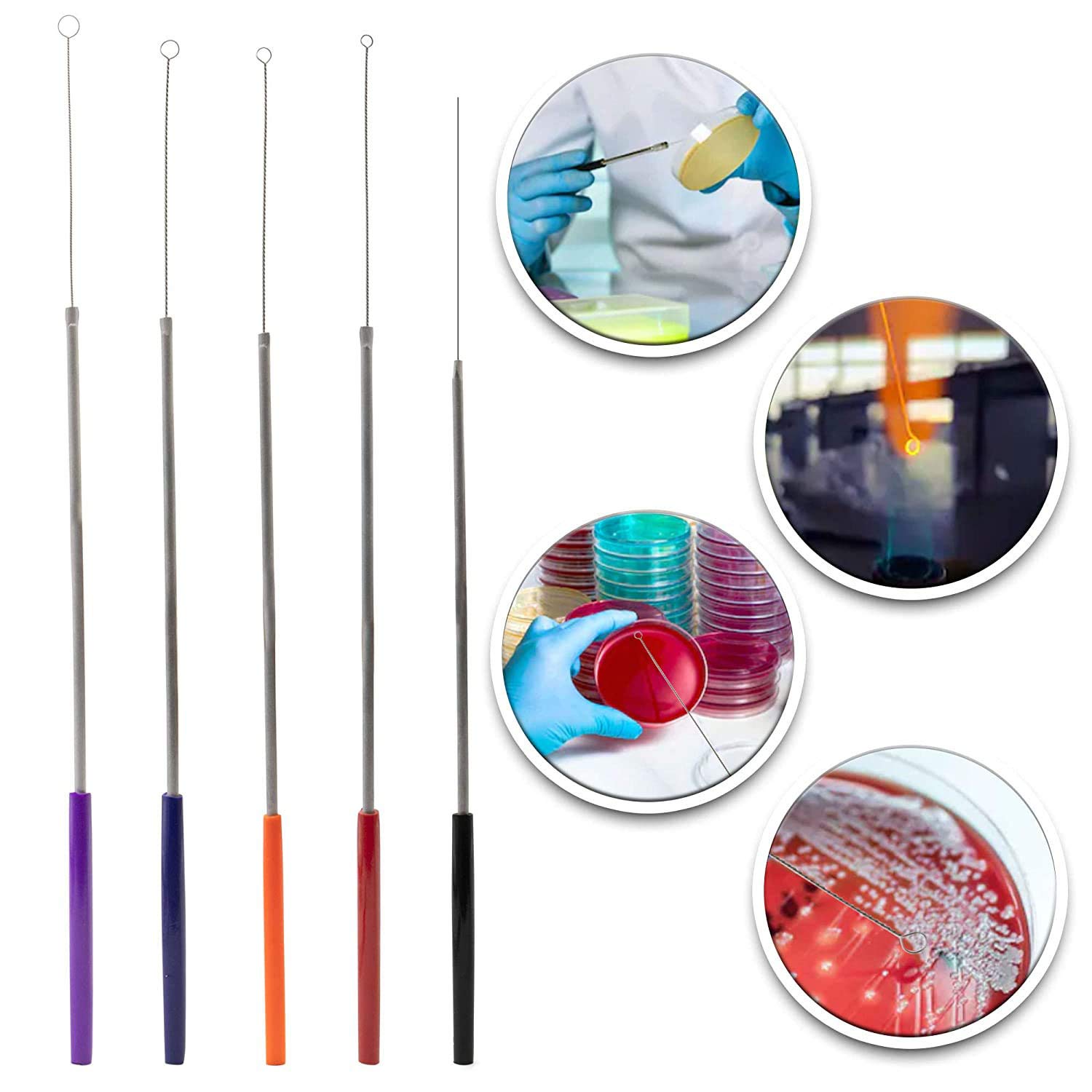







Scientific Labwares Reusable Inoculating Loops and Needle Set - Color-Coded Handle for Size Identification - Cell Streaking Lab Tools Perfect for Bacteria Cell Tissue Culture Lab
Share Tweet
Get it between 2025-01-23 to 2025-01-30. Additional 3 business days for provincial shipping.
*Price and Stocks may change without prior notice
*Packaging of actual item may differ from photo shown
- Electrical items MAY be 110 volts.
- 7 Day Return Policy
- All products are genuine and original
- Cash On Delivery/Cash Upon Pickup Available








Scientific Labwares Reusable Inoculating Loops and Features
-
BACTERIAL LOOP - Ideal for cell culture/streaking and transferring of microbiological samples
-
COLOR-CODED HANDLES - Conveniently identify loop diameter with ease (Red - 2mm, Orange - 3mm, Blue - 4mm, Purple - 5mm, Black - Needle).
-
SMEAR SMOOTHLY - Loops slide along agar surfaces without cutting or tearing material
-
REUSABLE LOOP - Two twisted astm-standard nichrome wire for added durability.
-
USAGE - Heat the loop until it glows then let it cool for about thirty seconds before touching your culture. Don't autoclave rather disinfect with ethanol. (Preferred)
About Scientific Labwares Reusable Inoculating Loops And
A streaker is used to spread bacteria on a culture medium, such as agar in a petri dish. In practice, a loop full of material is placed near one edge of the medium or agar and smeared back and forth to make a small but thickly smeared area which can then be studied to ascertain bacterial growth.




















